When filing your income tax return, one of the most significant reliefs available to salaried individuals comes under Section 16 of the Income Tax Act. This section allows for deductions from your salary income, reducing your overall taxable income and, as a result, the amount of tax payable.
Whether you're new to taxation or looking to make the most of available deductions, understanding Section 16 can help you plan your taxes better and legally save more.
What is Section 16 of the Income Tax Act?
Section 16 of the Income Tax Act provides three different types of tax deductions on salary income:
- Standard Deduction – A fixed deduction from your gross salary income.
- Entertainment Allowance – Applicable in certain cases, like for government employees.
- Professional Tax – Deduction of tax paid to state governments by employees.
The section allows salaried employees to reduce their taxable income without submitting additional investment proof. It's an automatic benefit provided during the computation of income under the "Salaries" head. "
Detailed Breakdown of Section 16 Deductions
Let’s go over the components that fall under this section in a little more detail:
- Standard Deduction under Section 16(i.a)
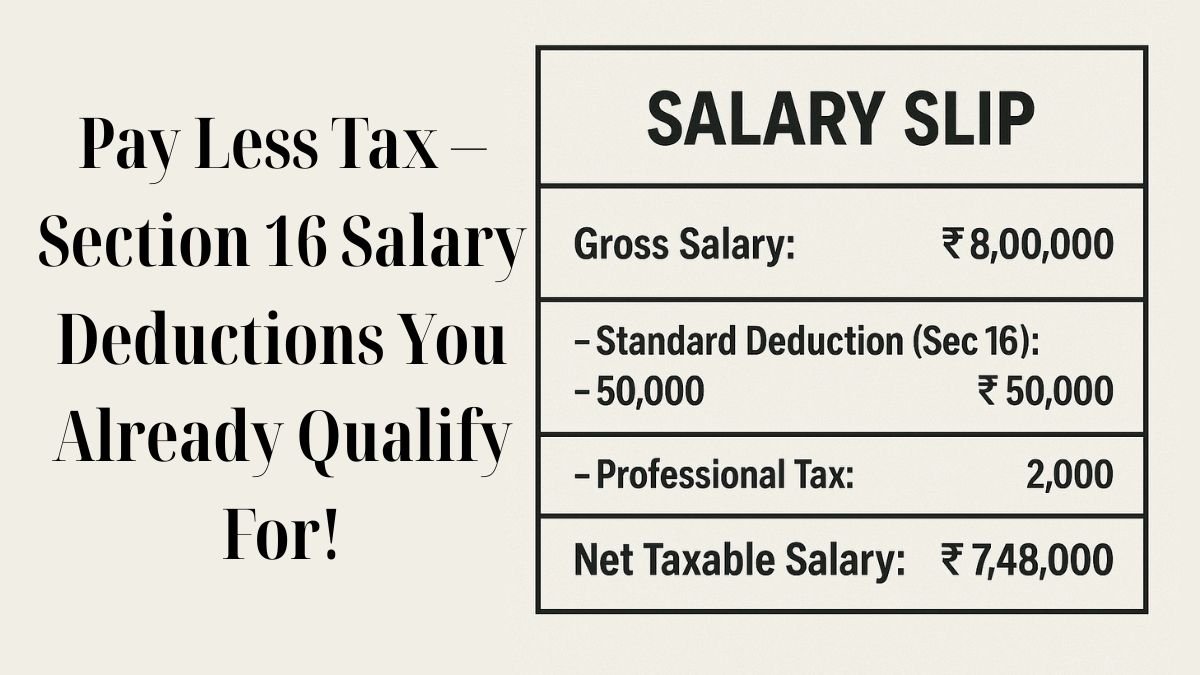
Introduced to simplify the deduction structure, the standard deduction under Section 16 of the Income Tax Act is currently fixed at ₹50,000 (as per AY 2023-24 onwards). This amount is subtracted from your total salary income before applying any tax rate.
Previously, salaried individuals had to claim transport & medical allowances separately. With the introduction of this standard deduction, things have become simpler & more beneficial.
- Entertainment Allowance under Section 16(ii)
This deduction is only available to government employees. It is not applicable to private sector employees.
The entertainment tax allowed as a deduction under section 16 is the least of:
- ₹5,000
- 20% of the basic salary
- Actual amount received as entertainment allowance
This provision ensures that the deduction remains modest & only helps offset expenses related to official duties. "
- Professional Tax under Section 16(iii)
Also known as employment tax, this is a tax levied by state governments. The maximum deduction allowed is ₹2,500 per annum. Section 16 provides a deduction for professional taxes paid by the employee, & it’s usually reflected in your payslip.
If your employer pays the professional tax on your behalf, you can still claim the deduction.
How Section 16 Helps You
This section is especially helpful for salaried individuals in the lower and middle-income brackets. Since it allows deductions from salaries without the need to submit investment proofs or purchase any specific financial product, it is universally accessible.
Also, since Section 16 of the Income Tax Act allows for deductions from your salary income at source, the benefit is applied automatically if your employer correctly computes your TDS (Tax Deducted at Source).
For instance:
If your gross annual salary is ₹6,00,000, you can claim a ₹50,000 standard deduction under Section 16(i.a). This means your taxable salary becomes ₹5,50,000 even before claiming any other deductions under Section 80C, 80D, etc.
Real-World Example
Let’s assume Mr. Arjun is a government employee earning ₹7,00,000 annually. He receives an entertainment allowance of ₹10,000 and pays ₹2,000 as professional tax.
Here's how Section 16 benefits him:
- Standard Deduction: ₹50,000
- Entertainment Allowance Deduction: Lesser of ₹5,000 (as per the rule)
- Professional Tax Deduction: ₹2,000
Total deduction under Section 16 = ₹57,000
So his taxable salary income = ₹7,00,000 – ₹57,000 = ₹6,43,000
Section 16 and the New Tax Regime
Under the new tax regime, standard deduction was initially not available. However, as per the Union Budget 2023, the standard deduction of ₹50,000 has been reintroduced even under the new tax regime for salaried individuals and pensioners.
This ensures that salaried taxpayers benefit from this section regardless of the regime they choose.
Conclusion
Section 16 of the Income Tax Act plays a pivotal role in helping salaried individuals lower their tax liability with minimal documentation and effort. It provides a deduction for professional taxes, entertainment expenses, and the standard deduction, making it a must-know for every taxpayer.
To summarise:
- It allows for deductions from your salary income easily.
- Helps reduce taxable income directly.
- Offers relief for salaried and government employees alike.
If you're filing your return, don’t forget to ensure your employer has factored in these deductions correctly, or make the claim while filing your ITR.











