When you make a payment to a professional for services rendered—be it a doctor, a lawyer, or even a software consultant—do you need to deduct TDS? The answer lies in Section 194J of the Income Tax Act, which outlines the specific provisions and obligations regarding TDS on professional services.
Let’s break it down simply so every business owner, CA, or individual payer can understand what’s expected and avoid penalties.
What is Section 194J?
Section 194J mandates that certain individuals or entities withhold TDS (Tax Deducted at Source) when they make payments for professional or technical services. TDS is deducted under Section 194J when payments are made to professionals like doctors, engineers, architects, chartered accountants, interior decorators, or consultants.
Whether you are a company paying a consultant or a hospital paying doctors for their time, the responsibility to deduct TDS lies with the payer, not the payee. "
When Does Section 194J Apply?
This section applies when:
- Payments are made for professional services,
- The total annual payment exceeds ₹30,000 (as per the threshold limit set),
- The payment is not for personal use.
TDS provisions relating to specific services are carefully defined under this section to cover not just professional services, but also technical services, royalties, & non-compete fees. "
Types of Services Covered
Section 194J provides the rules for deducting TDS on payments for scientific and skilled services. Here's a quick list:
- Legal, medical, engineering, architectural, and accountancy services
- Technical consultancy
- Interior decoration
- Advertising
- Film artist services
- Royalty and non-compete fees
The law is particularly focused on payments made to professionals for various services, as such payments are prone to tax evasion if not monitored through TDS.
Who Has to Deduct TDS?
TDS is deducted under Section 194J by:
- Companies
- Partnership firms
- Individuals/HUFs subject to audit under Section 44AB of the Income Tax Act in the preceding year
Even startups & small businesses should take this seriously if they cross the audit threshold.
What is the TDS Rate?
- For professional services: 10%
- For technical services (non-professional): 2%
- For royalty (in some cases): 10%
- For call centre services: 2%
If the PAN of the recipient is not available, the rate shoots up to 20%, as per Section 206AA. So, always collect PAN details from the professionals you are paying.
Exceptions to Note
There are certain cases where TDS under Section 194J is not applicable:
- If the aggregate amount paid or likely to be paid during the financial year does not exceed ₹30,000.
- If the payment is made by individuals or HUFs not liable to audit.
- Certain government bodies & exempt institutions.
However, these exceptions are limited. So always double-check before skipping TDS.
How and When to Deduct TDS?
TDS under Section 194J must be deducted at the time of credit of such sum to the account of the payee or at the time of payment, whichever is earlier. It must then be deposited with the government within the due date (typically the 7th of the following month).
Failure to deduct or deposit TDS can lead to:
- Interest under Section 201(1A)
- Penalty under Section 271C
- Disallowance of expense under Section 40(a)(ia)
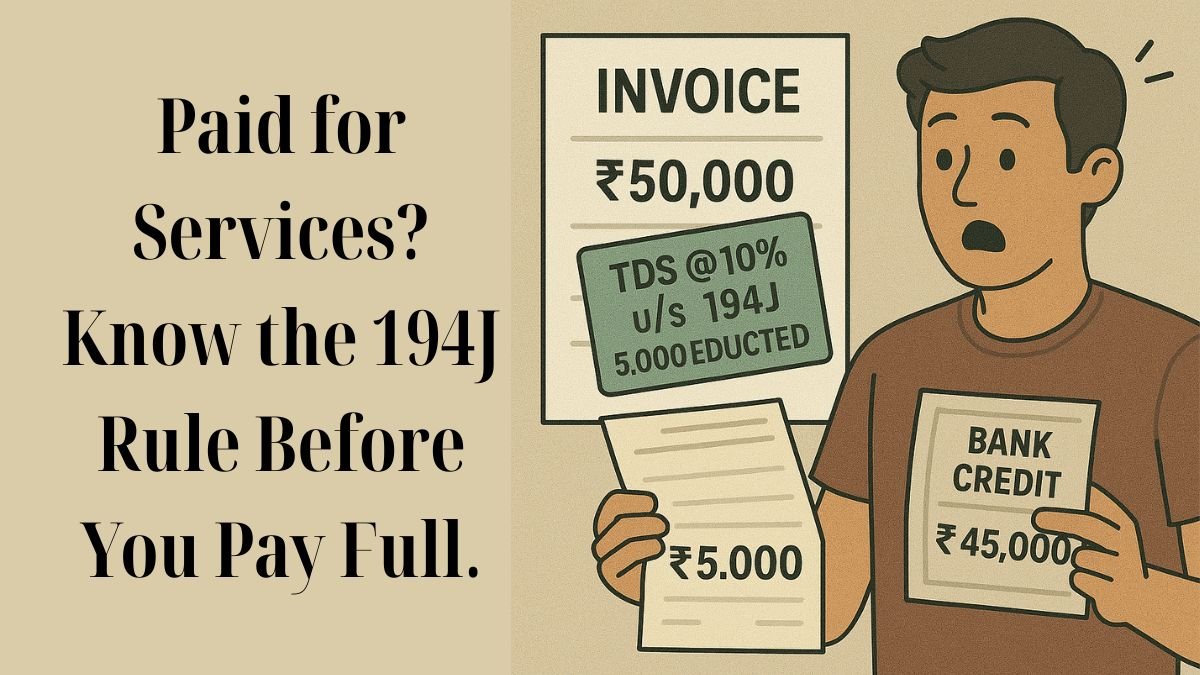
Practical Example
Let’s say you are running a digital marketing agency and you hire a freelance SEO consultant. You agree to pay ₹50,000 for a 2-month project. Since the payment exceeds ₹30,000, TDS at 10%, i.e., ₹5,000, must be deducted and deposited with the government. The consultant receives ₹45,000, and the ₹5,000 goes as advance tax under their PAN.
Failing to deduct and deposit this amount can cost you penalties and disallowance of the expense in your books.
Why Is Section 194J Important?
This section helps the government monitor large professional & technical transactions that may otherwise go untaxed. It ensures that the tax net includes high-value independent earners & service providers.
For businesses, compliance with Section 194J not only avoids legal trouble but also builds better documentation & transparency in financial operations.
Book your service now at Callmyca.com.











