Taxes are the backbone of any economy, and the Indian taxation system ensures steady revenue flow for the government. One of the key mechanisms for this is Advance Tax. Unlike the general belief that taxes are paid only at the end of the year during return filing, Advance Tax ensures that taxpayers contribute their share in advance, in regular intervals, based on their estimated earnings.
In simple words, Advance Tax is the amount of income tax that is paid much in advance during the same financial year in which the income is earned. This system avoids last-minute financial burden and helps the government manage cash flow effectively.
What is Advance Tax?
Advance Tax, also referred to as “pay-as-you-earn” tax, is a system under which taxpayers are required to calculate their income & pay taxes in parts throughout the financial year, instead of making a lump-sum payment at year-end.
It is applicable to:
- Salaried individuals (if TDS is not sufficient).
- Freelancers & professionals.
- Businesses (large and small).
- Investors earning significant capital gains, rental income, or other incomes.
Essentially, every person, whose estimated tax liability for the Financial Year is Rs. 10,000 or more, must pay Advance Tax in installments prescribed by the Income Tax Department."
Why Advance Tax is Important
Advance Tax plays a dual role. For taxpayers, it ensures they don’t face a heavy tax outflow at once. For the government, it assures consistent revenue throughout the year.
Benefits for Taxpayers:
- Prevents last-minute financial pressure.
- Reduces the chance of interest liability under Sections 234B and 234C.
- Encourages better financial planning.
Benefits for Government:
- Ensures regular revenue inflow.
- Helps fund public expenditure efficiently.
- Minimizes tax evasion, as payments are spread across the year.
Who Should Pay Advance Tax?
The obligation to pay Advance Tax applies broadly. It covers:
- Individuals (salaried, professionals, freelancers)
- Businesses and companies
- HUFs, partnership firms, and LLPs
- Investors with rental income, capital gains, or interest income
The golden rule is simple: if income tax payable in advance if tax liability exceeds Rs. 10,000, Advance Tax becomes mandatory.
Also Read: Why Paying Self-Assessment Tax is Non-Negotiable
Calculation of Advance Tax
Advance Tax calculation involves estimating your total income for the year, deducting allowable expenses, and applying applicable tax rates. Here’s how to do it step by step:
- Estimate Income – Include salary, business/profession income, rental, interest, capital gains, & other sources.
- Apply Tax Slabs – Use the applicable slab rates (old or new regime).
- Deduct TDS – Reduce any TDS already deducted by employers/banks.
- Final Liability – If the balance liability is Rs. 10,000 or more, you need to pay Advance Tax.
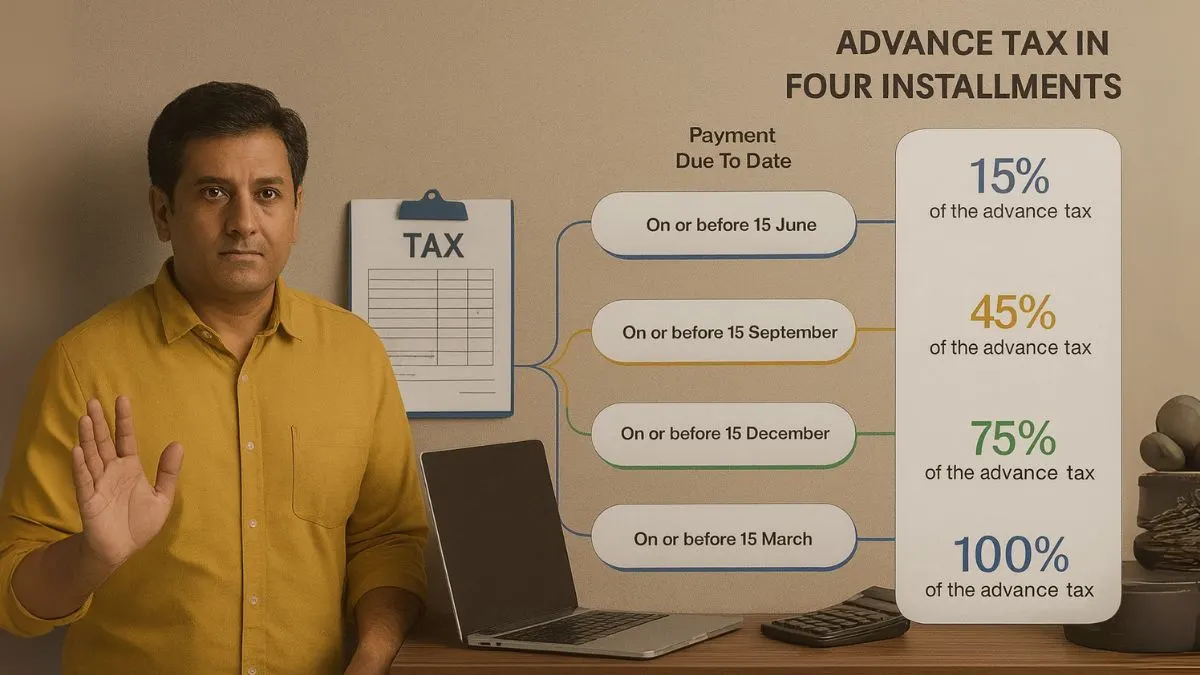
Advance Tax Due Dates and Installments
Advance Tax is not paid in one go. It is distributed into installments depending on the category of taxpayer:
For Individuals & Non-Corporates:
- 15% of total tax liability by 15th June
- 45% of total tax liability by 15th September
- 75% of total tax liability by 15th December
- 100% of total tax liability by 15th March
For Companies:
The same structure applies, but compliance is strictly monitored.
Even if you miss a due date, you can still make payments, but interest under Sections 234B and 234C may apply."
How to Pay Advance Tax
Advance Tax can be paid online and offline.
- Online (Preferred Method):
- Visit the Income Tax e-filing portal.
- Choose Challan 280.
- Fill in your details, PAN, and assessment year.
- Pay through net banking, UPI, or debit card.
- Offline:
- Visit an authorized bank branch.
- Fill Challan 280 manually and deposit the tax.
Payment details are automatically updated and reflected during e-Filing of Income Tax Return or Forms.
Also Read: Capital Gains, Deductions & Computation Explained
Consequences of Non-Payment of Advance Tax
If you fail to pay Advance Tax or pay less than required, you may face penalties in the form of interest:
- Section 234B – Interest for default in payment of Advance Tax.
- Section 234C – Interest for deferment of installment payments.
Thus, timely payment saves both money & stress.
Advance Tax for Different Income Sources
- Salaried Employees: Most salaried employees do not need to worry since employers deduct TDS. However, if you earn from other sources like capital gains or rent, and your liability exceeds Rs. 10,000, you must pay Advance Tax separately.
- Businesses and Professionals: They must carefully estimate annual income. Advance Tax applies irrespective of business size. Presumptive taxpayers under Sections 44AD/44ADA pay the entire Advance Tax in one installment by 15th March.
- Investors: Those earning dividends, rental income, or capital gains must pay. Even short-term stock traders are covered.
Common Mistakes to Avoid
- Underestimating Income – Leads to underpayment and penalties.
- Ignoring Non-Salary Income – Rental, capital gains, or interest often get missed.
- Missing Due Dates – Even small delays trigger interest liability.
- Not Reconciling with Form 26AS – Always cross-check taxes paid against your PAN.
Advance Tax vs Self-Assessment Tax
Many confuse Advance Tax with Self-Assessment Tax. Here’s the difference:
- Advance Tax – Paid in advance, during the year, based on estimated income.
- Self-Assessment Tax – Paid after the year ends, when filing the return, to cover any shortfall.
Together, they ensure full payment of your liability.
Advance Tax in e-Filing of ITR
When you pay Advance Tax, the details are reflected in your Form 26AS / AIS. At the time of e-Filing of Income Tax Return or Forms, you must include this information. If excess tax is paid, it will be refunded after processing.
This seamless link between Advance Tax and return filing makes compliance easier & avoids duplication of efforts.
Also Read: Presumptive Income Scheme for Small Businesses
FAQs on Advance Tax
- Who needs to pay Advance Tax?
Any person whose estimated tax liability is Rs. 10,000 or more in a financial year. - What happens if I don’t pay?
Interest under Sections 234B and 234C will apply. - Can salaried people be liable?
Yes, if they earn from capital gains, rent, or other income beyond salary. - Can Advance Tax be revised?
Yes, taxpayers can make multiple payments if estimates change. - Is Advance Tax refundable?
Yes, any excess payment will be refunded.
Conclusion
Advance Tax ensures that the government collects revenue steadily while reducing the end-of-year burden for taxpayers. It is the income tax payable in advance if tax liability exceeds Rs. 10,000, and every person, whose estimated tax liability for the Financial Year is Rs. 10,000 or more, must pay it. The system of installments & easy e-Filing of Income Tax Return or Forms makes it convenient and transparent.
👉 Want to avoid penalties and file your Advance Tax smoothly? Get expert help from Callmyca.com for stress-free tax planning and filing.











