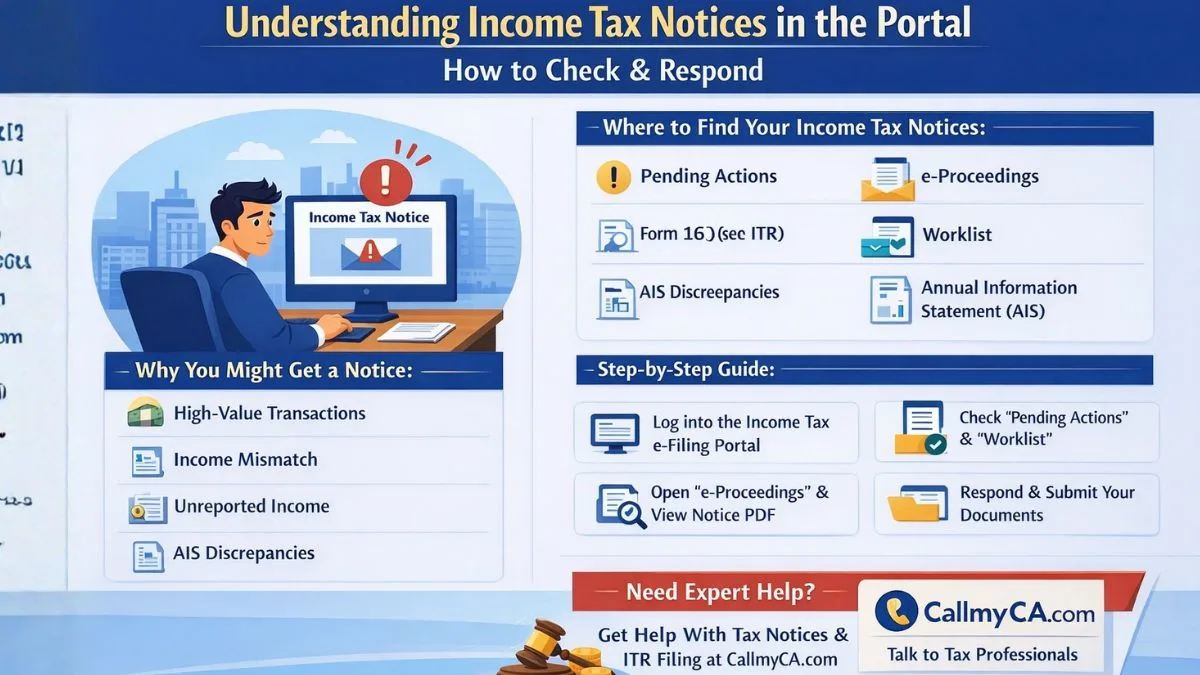
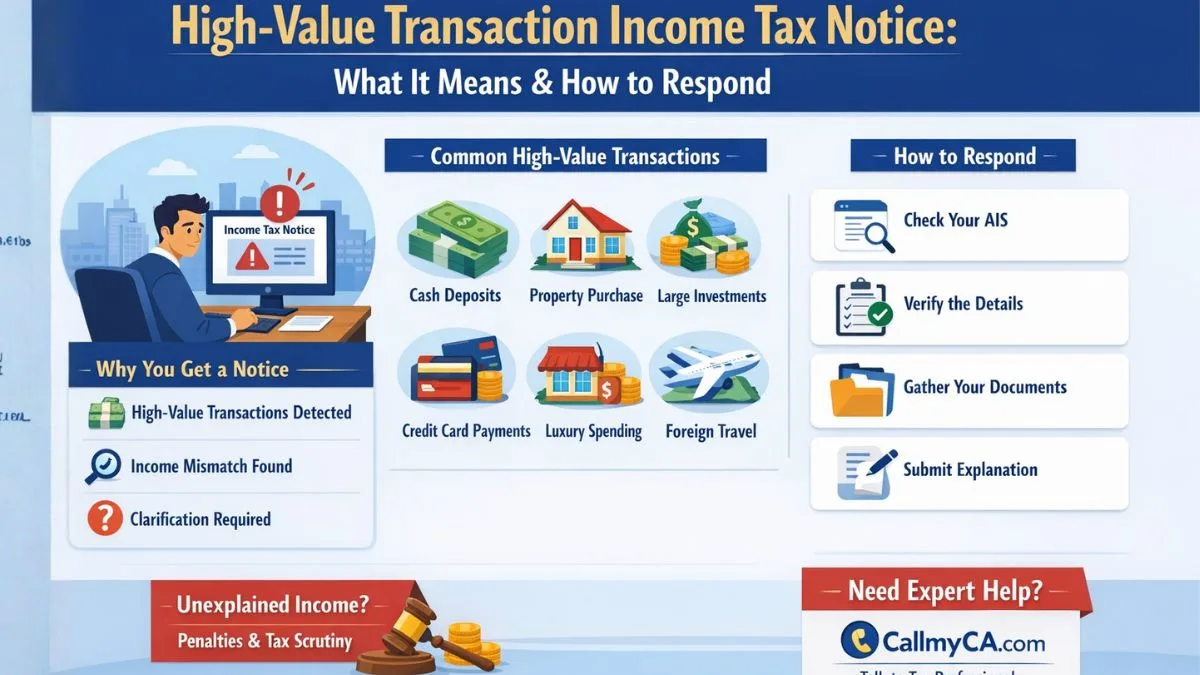
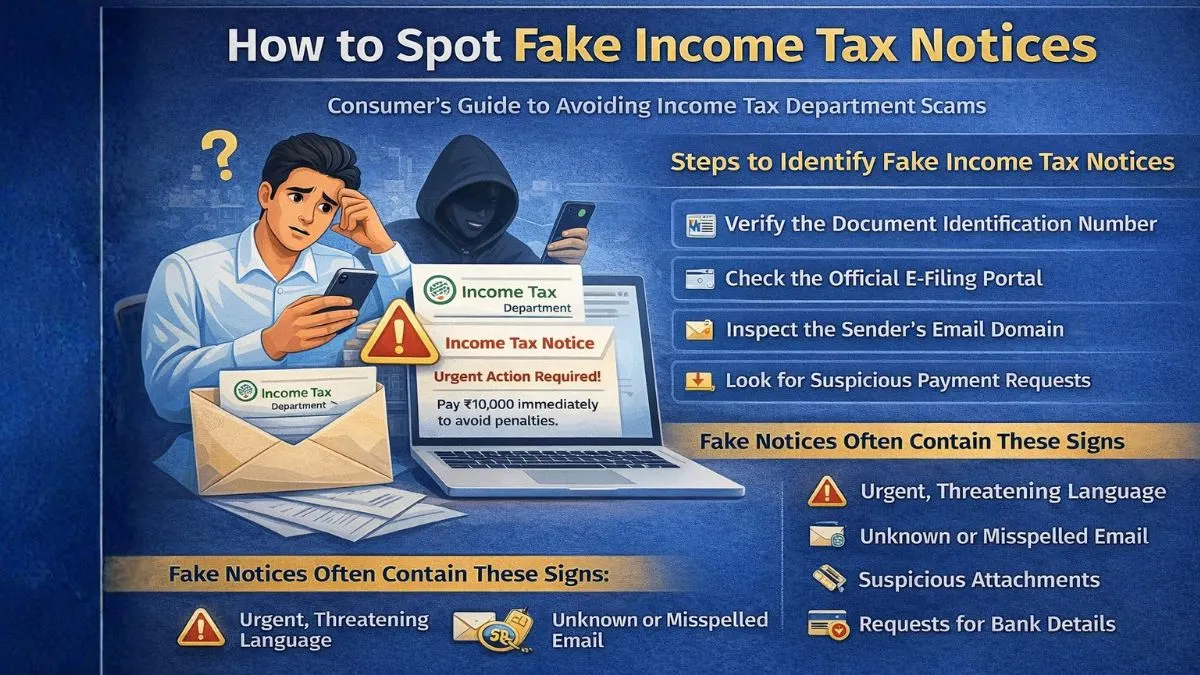
The Indian Income Tax Act provides several exemptions to encourage growth, development, and smooth functioning of certain entities that serve a larger purpose. One such provision is Section 10(23A) of the Income Tax Act, 1961. This section specifically exempts certain incomes received by specific entities from income tax, subject to conditions. The idea behind this section is to support professional institutions, associations, and other notified bodies that work towards advancing particular professions or sectors in India.
Understanding Section 10(23A) is crucial for taxpayers, associations, and professionals, as it clarifies what kind of incomes are exempt & under what circumstances. It is not a blanket exemption, but rather one that comes with conditions on utilization and application of funds.
Scope of Section 10(23A)
The Income Tax Act is structured to provide relief to institutions that are non-profit in nature & contribute to professional growth. Section 10(23A) provides a list of incomes exempt from taxation, but only when earned by notified professional associations & institutions.
For example, professional councils, associations related to medicine, law, accountancy, engineering, or other notified groups may qualify under this section. The exemption covers income derived from membership subscriptions, grants, or other specified sources. However, such institutions must apply the income for the benefit of their members and not for private profits.
From registration to renewal and annual compliance, we safeguard your institution’s tax-free status at every stage. 👉 click here
Application of Income – A Key Requirement
One of the most important aspects of Section 10(23A) is the way income must be utilized. The law requires that the assessee shall apply its income, or accumulate the income for application, solely towards the objects for which the institution is established.
This means the exempt income cannot be diverted for unrelated activities or distributed among members as profit. Instead, it must be used for promoting the professional cause of the body. Institutions that fail to meet this condition may lose their eligibility for exemption under this section.
Entities Covered under Section 10(23A)
The exemption is not open to all entities. It is restricted to professional institutions or associations that are specifically notified by the government. Some common categories include:
- Professional Councils – like medical councils, bar councils, or accountancy institutes.
- Associations – formed for the regulation, development, & advancement of specific professions."
- Notified Bodies – entities recognized by the government to carry out professional work in the public interest.
These entities enjoy exemption on specified incomes as long as they abide by the conditions of application & accumulation.
Also Read: Tax Exemption for Educational and Medical Institutions
Why Section 10(23A) Matters
The Indian government recognizes that professional bodies play a key role in shaping skilled manpower, maintaining standards, & protecting public interest. Exempting certain incomes received by specific entities from income tax helps them focus more on their mission rather than worrying about tax liabilities.
For instance, medical councils use their funds for setting ethical standards in healthcare. Bar councils work towards regulating legal practice. Similarly, accountancy bodies train professionals & maintain financial integrity. By providing exemptions, the law ensures that these institutions remain financially sound and capable of serving society.
Conditions for Claiming Exemption
Entities cannot claim this exemption automatically. They must satisfy specific conditions:
- Income must be from sources relevant to the professional body.
- The income must be applied or accumulated for professional objects.
- Accounts should be maintained transparently.
- The body should not distribute profits to its members.
Failure to meet these conditions may attract taxation under normal provisions of the Act.
Most institutions assume their income is automatically exempt. In reality, one compliance miss can cancel the benefit. Curious if yours is safe? 👉 click here
Examples to Understand Better
Imagine a Medical Council that collects membership fees from doctors. This amount is used to conduct training programs & regulate professional standards. Since the income is applied for the objectives of the institution, it qualifies for exemption under Section 10(23A).
On the other hand, if the same council uses part of its income to invest in unrelated commercial activities for profit, it may lose exemption benefits. Thus, compliance with conditions is critical.
Relationship with Other Exemptions
Section 10(23A) must not be confused with other exemptions like Section 10(23C), which provides relief to educational institutions & hospitals. While both sections focus on exempting incomes of entities serving a public purpose, the scope of Section 10(23A) is narrower & applies mainly to professional bodies.
Judicial Views on Section 10(23A)
Courts in India have consistently upheld the principle that provides a list of incomes exempt from taxation is to be interpreted in the spirit of promoting professional advancement. However, they have also stressed that misuse of funds or deviation from stated objectives can result in denial of exemption.
For example, in cases where professional associations diverted funds for private gains, courts ruled against granting exemption. This reinforces the importance of transparent application of income.
Also Read: The Exemption Rule Powering Mutual Funds & UTI
Challenges in Implementation
While Section 10(23A) offers relief, institutions face certain challenges:
- Strict compliance requirements.
- Ambiguity in defining "professional objects."
- Regular scrutiny by tax authorities."
- Need for clear documentation and audit reports.
These challenges highlight the importance of proper tax planning & professional guidance for such institutions.
Conclusion
Section 10(23A) of Income Tax Act is a specialized provision that exempts certain incomes received by specific entities from income tax. It applies to professional institutions & associations that work towards advancing particular professions. The key requirement is that the assessee shall apply its income, or accumulate the income for application, solely towards professional objectives. By doing so, these bodies get tax relief and continue to play their vital role in society.
For taxpayers and professionals associated with such institutions, understanding Section 10(23A) is essential. It ensures compliance while also maximizing the benefits provided by the Income Tax Act.
👉 Want to know how to legally maximize exemptions & save tax for your institution? Click here to connect with experts at Callmyca.com – your trusted partner for professional tax planning.